QAny precautions or preparations needed before doing the Maternal Blood 45 Y-DNA Test ?
No special precautions or preparations are needed. Fasting is not required as well.
QHow much blood is needed for Maternal Blood 45 Y-DNA Test ?
12ml of blood from the expected mother
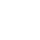
QHow does the Maternal Blood 45 Y-DNA Test report look like?
For Maternal Blood 45 Y-DNA Test report:
QUnder what circumstances is the expected mother NOT able to do the Maternal Blood 45 Y-DNA Test?
Clients, who are an organ transplant recipient, are not qualified to take the test. (DiagCor will NOT accept the case)
QDo I need an empty stomach before taking the test?
No special preparation is required, no fasting.
QWhen will clients receive the report for the test?
In about 18 working days after DiagCor receive all the samples.
QWhen is the suitable time for expected mother to do the test?
10 weeks pregnant or above (subject to ultrasound examination)
QWhat do I need to prepare before Non-invasive Prenatal Paternity Test (MBT), do I need to draw blood on an empty stomach?
No special preparation required, no fasting required
QUnder what circumstances one cannot take Non-invasive Prenatal Paternity Test (MBT)?
Surrogacy、Fetal proportion should not be less than 2% (not less than about 6-8 weeks of pregnancy) and Fraternal twins
QWhat do I need to prepare for the Fragile X Syndrome Test (AFE), do I need an empty stomach?
No special preparation is required, no fasting.
QUnder what circumstances can this genetic test not be done?
If the subject has undergone organ transplantation, they cannot accept this test. (DiagCor will not accept this sample for testing)
QI have no obvious symptoms, why do I need to conduct Fragile X syndrome test?
-
- Even if women show no symptoms, they may still be carriers, and have chance to pass mutated gene towards their next generation.
- If you give birth to a girl, she has chance to become a fragile X syndrome carrier. If you give birth to a boy, he has chance of being a fragile X syndrome patient.
QWho needs to be tested for Fragile X syndrome?
1. Someone in the family has symptoms of tremor after the age of 50
2. The family has a history of autism
3. The family has a history of intellectual development or growth retardation
4. The family has a history of fragile X syndrome
5. The family has a history of premature ovarian failure or premature menopause
6. Worried about the child suffering from fragile X syndrome (expectant mother / pregnant lady)
** Apart from expectant mothers who can receive the fragile X carrier test to protect the health of the next generation, it can also be suitable for all women who are preparing for pregnancy as part of the pre-marital examination
QCan I do this test if I am beyond 14 weeks pregnant?
It is recommended that you check with your doctor first. For pregnancy on or
after 20 weeks we can also provide screening (MP2) and/or a short-term prediction
(MPX). The report will be available within one working day.
QWill there be any aftereffect to pre-eclampsia?
Studies show that pregnant women with pregnancy toxemia are twice as likely to also have cardiovascular disease and hypertension than other mothers. Premature babies generally have poor resistance and immunity, which can lead to stunting.
QIf you have had pregnancy toxemia during pregnancy, is there a high chance of having it again in the future?
Women who have suffered from pregnancy toxemia during pregnancy in the
past have higher chances of developing it again in any subsequent pregnancy. But because of individual differences, early pre-eclampsia screening is recommended for every pregnancy in between 11- and 14-week.
QWhat does the report mean as low or high risk?
If risk is low, it means that you are less likely to develop pregnancy toxemia during pregnancy. Conversely, if you have a high risk means that the chances of developing the disease during pregnancy are quite high. Doctors can start the intervention earlier and monitor pregnancy more closely to reduce the impact of the disease to the mother and the fetus.
QWhen is it appropriate to do this test?
It is especially recommended for pregnant women from the 11th to the 14th week of pregnancy to test. If you can be found as a high-risk pregnant woman before the 14th week, you can seize the golden time of treatment and reduce the premature birth rate by up to 80%.
QWhy choose this Pre-eclampsia screening?
This screening meets the international standards for early pre-eclampsia (refer
to the latest guidelines of FIGO and FMF), and can accurately predict the risk of
developing pregnancy toxemia.
QWhy expected mothers are strongly recommended to take the Maternal Blood Y-DNA test?
It is because if the expected mother is a carrier of an X-linked dominant disorder, there will be 50% chance of inheritance if the expected baby is a male. X-linked dominant disorders include diseases such as amblyopia, epilepsy, mental retardation and other diseases such as Fragile X syndrome. Fragile X syndrome is regarded the cause of different growth problems with regard to learning abilities as well as delayed development of speech. Therefore, by taking the Maternal Blood Y-DNA test, the sex of the expected baby can be verified. Expected parents can determine the necessity of taking further tests such as Fragile X Carrier Screening (MFX).
QI have filled in my contact no. on the test request form, why I still could not check the authority of my report?
Our data base would be updated once an hour, please try an hour later.
QUnder what circumstances is the expected mother NOT able to do the Maternal Blood 70 Y-DNA Test?
Clients, who are an organ transplant recipient, are not qualified to take the test. (DiagCor will NOT accept the case)
QWhat is Y-chromosome?
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or absence of Y that determines the male or female sex of offspring produced in sexual reproduction.
Source: Wikipedia
QHow does the Maternal Blood 70 Y-DNA Test report look like?
For Maternal Blood 70 Y-DNA Test report:
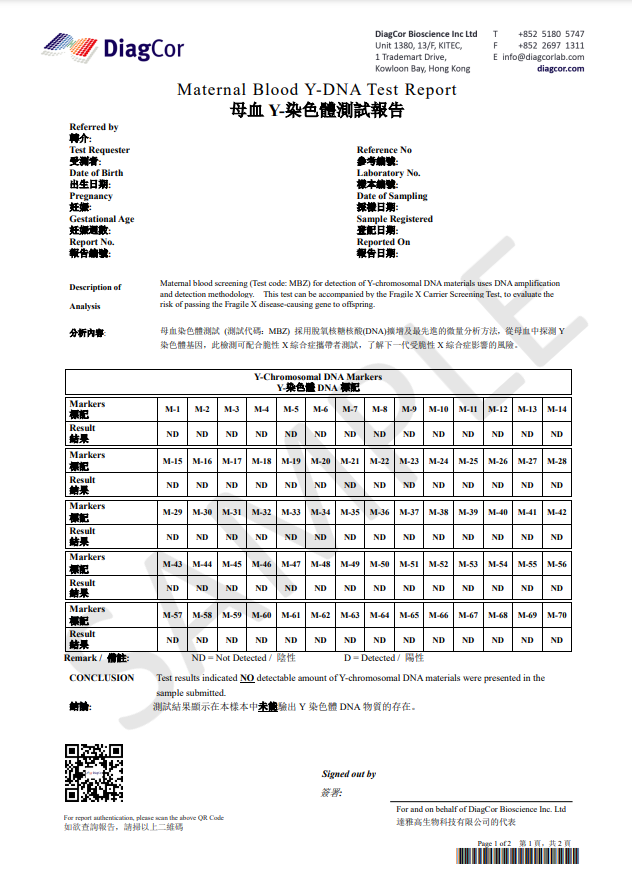
QAny precautions or preparations needed before doing theMaternal Blood 70 Y-DNA Test ?
No special precautions or preparations are needed. Fasting is not required as well.
QHow much blood is needed for Maternal Blood 70 Y-DNA Test ?
12ml of blood from the expected mother
QWhat is the difference between legal use and non-legal use Postnatal paternity testing?
The test methods are the same. For paternity test for legal purposes, samples must be collected at DiagCor Laboratory. All identity documents of the testees need to be checked and recorded. For paternity test without legal use, there is no restriction on the location of the sample collection, and there is no need to check the identity of the testees.
QWhat are the possible results for Postnatal Parentage Testing report?
The report has two results:
- Not excluded - most likely a biological father
- Excluded - not a biological father
QIs the test accuracy of taking buccal sample same as taking the blood sample?
Yes, they are the same. Because all cells in one body have the same DNA.
QIs there any age limits for a child to attend Postnatal Parentage Testing?
There are no restrictions.
QDo DiagCor have branches in Shen Zhen?
No. DiagCor Bioscience Inc. Ltd. is located in Hong Kong. In addition, DiagCor Bioscience Inc. Ltd is one of the subsidiaries of Pangenia Group.
QWhen will clients receive the report for the Maternal Blood Y-DNA Test (MBY) + Y-chromosome DNA Exclusion (MBE)?
In about 5 working days after DiagCor receive all the samples.
QWhat are the limitations of Y-chromosome DNA exclusion (MBE)?
- Maternal blood Y-DNA test (MBY) should be done before conducting Y-chromosome DNA Exclusion (MBE). If the MBY test results indicate that there is a detectable amount of Y-DNA in the sample submitted, then the expected mother can proceed to take MBE test.
- If there are more than one alleged fathers and they share the same paternal line (such as brothers, uncle & nephew, grandfather & grandson, etc.), the results would be “Non-Exclusion”.
QWhen is the suitable time for expected mother to do the Maternal Blood Y-DNA Test (MBY) + Y-chromosome DNA Exclusion (MBE)?
7 weeks pregnant or above (subject to ultrasound examination)
QAny precautions or preparations needed before doing the Fragile X Carrier Screening (MFX) test?
No special precautions or preparations are needed. Fasting is not required as well.
QWhen will clients have the report for Fragile X Carrier Screening (MFX) after DiagCor received the samples?
In about 1 working day after DiagCor received all the samples
QHow much blood is needed for the Fragile X Carrier Screening (MFX)?
12ml blood of the expected mother
QWhen is the suitable time for expected mother to do Fragile X Carrier Screening (MFX)?
7 weeks pregnant or above (subject to ultrasound examination)
QWho needs fragile X syndrome testing?
- If the family has a history of tremor symptoms after 50 years old
- If there's family history of autism
- If the family has a history of intellectual development problems or slow growth
- If the family has history of fragile X syndrome
- If the family has a history of ovarian failure or early menopause
- If you are concerned about the possibility of your children inheriting fragile X syndrome (being a mother / prospective mother)
** In addition to the prospective mothers who want to take the fragile X carrier test to protect the health of their next generation, it can also be suitable for all pregnant women, as part of the prenatal check.
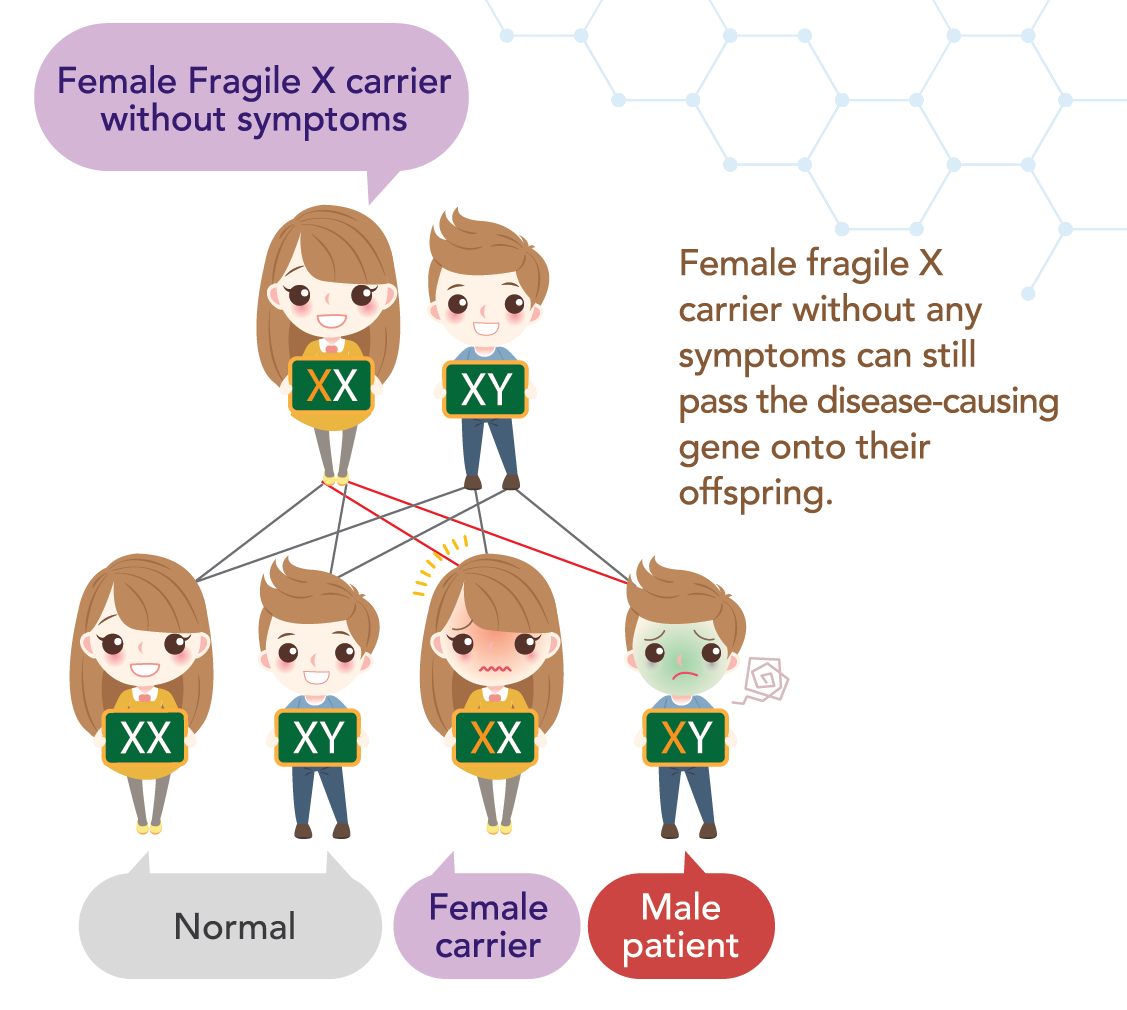
QI have no obvious symptoms, why do I need to be tested for Fragile X carrier (MFX)?
- Even if women show no symptoms, they may still be carriers, and have chance to pass mutated gene towards their next generation.
- If you give birth to a girl, she has chance to become a fragile X syndrome carrier. If you give birth to a boy, he has chance of being a fragile X syndrome patient.
The abovementioned claims can be explained in the following diagram:
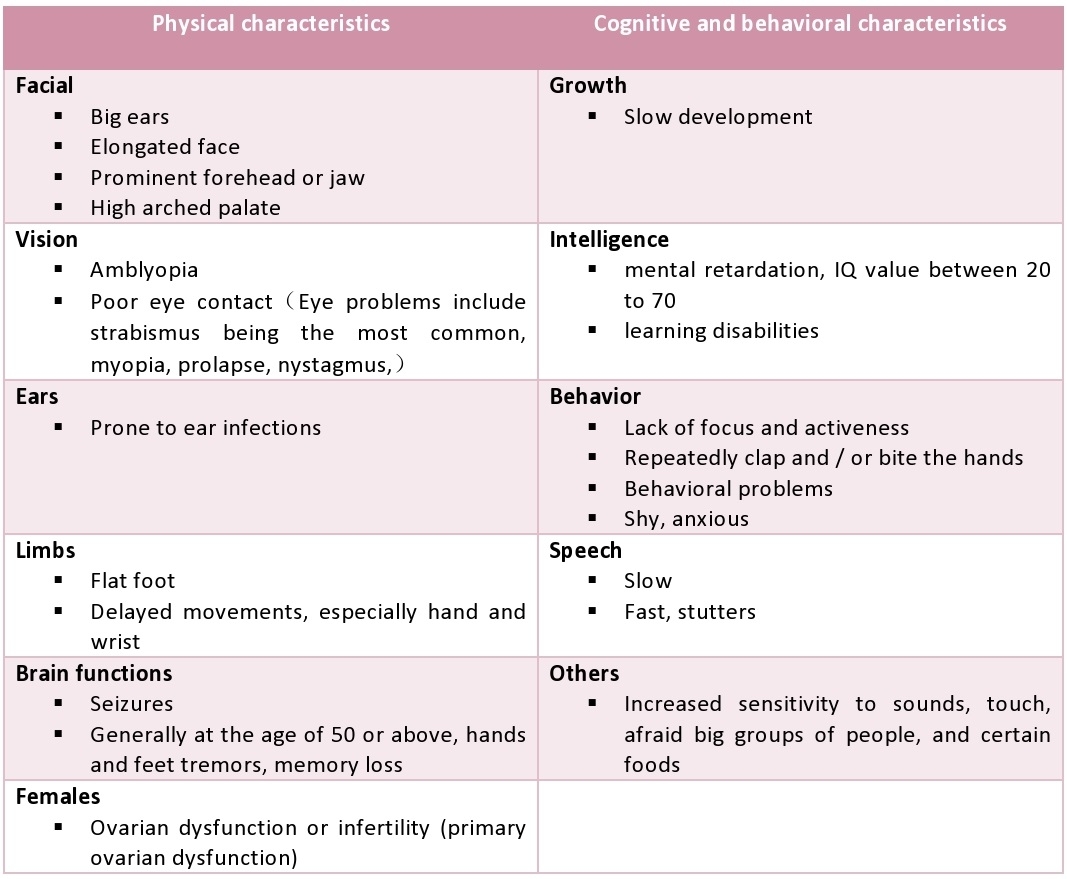
QWhat are the common features of Fragile X syndrome?